Adaptive Headlights Explained

Between limited visibility, potential drowsiness, and a higher risk of drunk drivers, nighttime can be a dangerous time to be behind the wheel.
While traditional headlights provide illumination, they have their limitations. Adaptive headlights enhance the range and responsiveness of a vehicle’s headlights as your driving conditions change to help you navigate during nighttime trips.
As with any other advanced driver-assistance system, adaptive headlights are not a substitute for staying alert and paying attention while driving at night. That being said, let’s explore what adaptive headlights are, how they work, and how they should be used.
What are adaptive headlights in car and how do they work?
Adaptive headlights are commonly applied to headlights to do one or more of the following:
● Change the horizontal angle according to the steering wheel inputs
● Change the vertical angle according to the vehicle load
● Switch automatically between low and high beams
● Vary the light beam to different areas ahead of the vehicle
Regardless of which function(s) the lights have, each is designed to improve visibility to the driver while minimizing glare to other vehicle drivers on the road.
Based on a variety of inputs such as steering wheel angle, cameras, speed sensors, and so on, adaptive headlights can take into account factors like the curvature of the road, the vehicle’s position in relation to nearby vehicles, and the vehicle’s load.
For instance, if another vehicle is approaching from the opposite direction or is right in front of your vehicle, adaptive headlights can adjust the headlights to help ensure they don’t blind the oncoming driver (using a High Beam Control System), or if the vehicle is making a turn, these headlights can extend headlight coverage by pivoting the lights in the direction of the turn so that it illuminates more of the road in front of the vehicle. Adaptive headlights can even take into account hilly terrain, helping ensure that light constantly shines on the road ahead even as the car drives over a speed bump or slope.
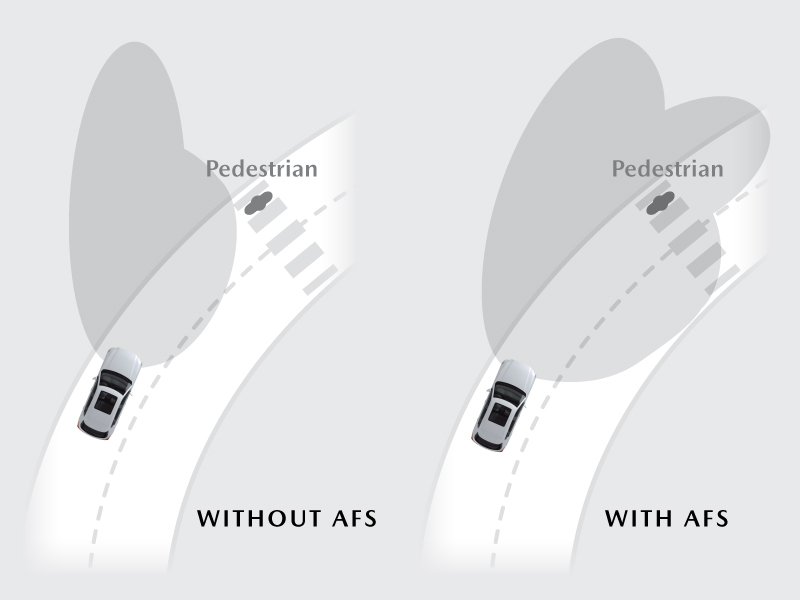
Illustration displayed for feature explanation only.
Components of typical adaptive headlights
How a particular adaptive headlight system works will vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle, but the following components are commonly used in AFS systems:
● LED drivers: LED lights are often used because they’re energy-efficient, bright, and adjust faster to current changes — around two times faster than incandescent bulbs. LED drivers are circuits that ensure optimal illumination by managing the power supply (and thus the brightness) of each individual LED.
● LED Matrix Manager: Where LED drivers help maintain brightness, LED matrix managers help dim certain LEDs using pulse duty cycles, which adjust the light intensity of each bulb. This allows fine-tuning of where the light is projected.
● Stepper motors: Stepper motors are responsible for adjusting the position of the LED lamps according to information gathered from sensors that detect the car’s speed, steering wheel position, road topography, load, and surrounding vehicles.
● Imaging sensors: These sensors pick up information regarding the distance from and speed of other vehicles, then converts these inputs into electrical signals for the adaptive headlights to react to.
● Multipoint control unit: Essentially the brain of an adaptive headlight system, the multipoint control unit (MCU) ensures all components work seamlessly with each other and coordinates all electrical messages sent to the system.
Again, your vehicle may include more unique components depending on its make and model. Be sure to refer to your owner’s manual for more information.
There are limitations to the range and detection of the system. Please see your Owner’s Manual for further details.
Advantages of adaptive headlights
Here’s why adaptive headlights may benefit you, particularly if you work late-night shifts or travel often during the evening hours:
1. Better visibility and consideration of other cars on the road
Traditional headlights provide a fixed field of illumination. Consequently, when a vehicle turns on a curved road, certain areas won’t be visible. There’s also the risk, when high beams are activated, of the lights unintentionally entering the sightline of oncoming drivers and momentarily blinding them. Adaptive headlights address these limitations by pivoting lights into a turn and expanding the range of illumination ensuring improved coverage as the vehicle maneuvers.
2. Improved safety
The ability to see better and further down the road can help boost reaction times and avoid accidents if drivers remain attentive and alert while driving. This is especially crucial because the risk of being in a fatal accident increases threefold at night, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
3. Reduced glare
Nighttime driving conditions can be exacerbated when bright headlights reflect off rearview mirrors and create a glare. Adaptive headlights can help alleviate this problem by either dimming certain LEDs or adjusting their direction away from other drivers.
Although adaptive headlights are incredibly helpful, it’s crucial to remain aware of your surroundings while driving, including areas that are poorly lit. Note that adaptive headlights do not necessarily include automatic high beams, although some systems may include this feature as part of their mechanism. As stated previously, always consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for information regarding how adaptive headlights work in your exact make and model.
Adaptive Headlights in Mazda vehicles
Our AFS system is part of our i-Activsense® Safety Technology suite that’s available in models like the agile Mazda CX-30, the sleek Mazda3 Sedan, and the off-road-ready Mazda CX-50.
For more information, check out our comprehensive safety features article.
Shopping for vehicles built with safety in mind? Explore the newest vehicles at Mazda.
At Mazda, we believe confident driving leads to better driving. Our Safety Technology is designed to help prevent and mitigate accidents, providing drivers with added insight for better awareness, responsiveness, and peace of mind. In fact, our Safety Technology has helped many of our models earn IIHS TOP SAFETY PICK awards.
To experience the Mazda commitment to safety, schedule a test drive at a dealer near you today.
Learn More About Safety Features:
● Lane Departure Warning and Lane-Keep Assist
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and is based on the latest competitive information available at the time of posting. Information herein is subject to change without notice and without Mazda incurring any obligations. Please review a variety of resources prior to making a purchasing decision. Visit Resource Center for more articles.




















